
afro.who.int
Bamako, 7 September 2015 – A case of circulating vaccine-derived poliovirus type 2 (cVDPV2) has been confirmed in Bamako, the capital and largest city of Mali. The country is on high alert after national authorities detected a paralysis case with onset 20 July 2015. The patient is a 19-month old child of Guinean nationality whose paralysis occurred 7 days prior to the child’s arrival in Bamako to seek health care. The last case of wild polio virus (WPV) in Mali dates back to June 2011 in Goundam, Timbuktu Region.
The current detected virus is genetically linked to a confirmed VDPV detected in Siguiri district, in the Kankan Region of Guinea in August 2014, and has been circulating across international borders for more than 2 years without detection.
The risk of spread of this virus is deemed high and it has the capacity to cause paralytic disease in humans or kill. The emergence and circulation of VDPV2 reveals low population immunity against the virus due to low rates of vaccination coverage in Guinea. Consequently, oral polio vaccine (OPV) must be administered multiple times to stop the outbreak and protect children.
Problem, Solution, SitRep, or ?:
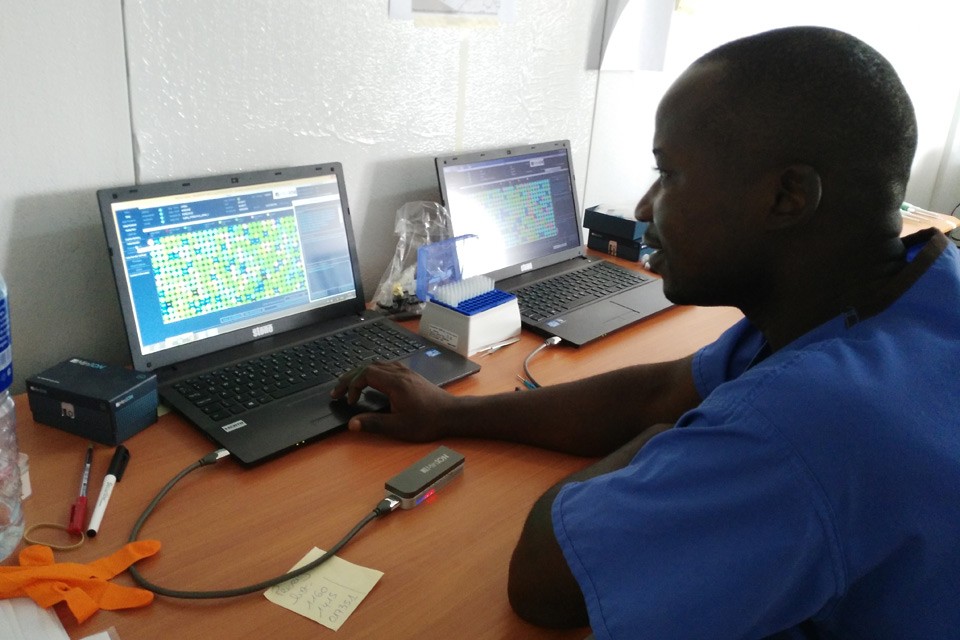






 Samples from the Ebola epidemic in West Africa are held by public-health agencies in the region and abroad. Daniel Berehulak/NYT/Redux/Eyevine
Samples from the Ebola epidemic in West Africa are held by public-health agencies in the region and abroad. Daniel Berehulak/NYT/Redux/Eyevine
Recent Comments